Hazards and Disasters Information
Hazards and Disasters
Hazard is a dangerous phenomenon, substance, human activity
or condition that may cause loss of life, injury or other health impacts,
property damage, loss of livelihoods and services, social and economic
disruption, or environmental damage.
Hazards can be Natural or Synthetic. It can be geological,
sea or hydrometeorological.
Natural events are anything that is caused by natural
process. For example, rain and wind.
Some natural events become extreme and can be of risk to
people and properties. For example, heavy rain might cause flooding.
When does a hazard become a disaster?
Hazards become disasters when a hazard causes serious
disruption of the functioning of a community or a society involving widespread
human, material, economic or environmental losses and impacts, which exceeds
the ability of the affected community or society to cope using its own
resources.
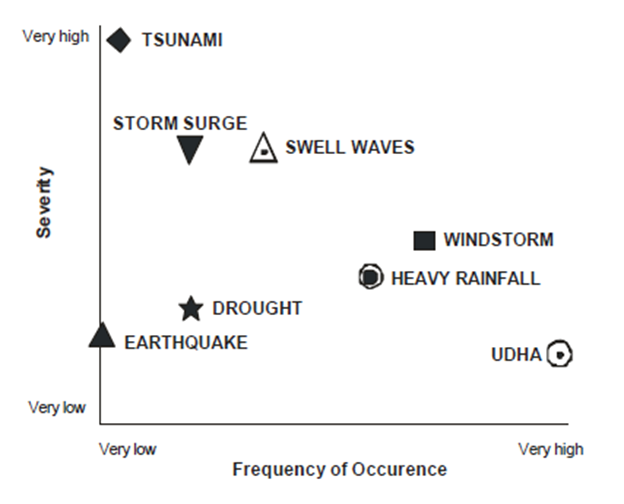
Maldives has many natural hazards such as:
- Cyclones
- Floods due to Heavy Rainfall
- Swell Wave
- Storm Surges
- Tsunami
- Earthquake
- Drought (water shortage)
- Fire
Hazard Pattersn of Maldives
cyclones
Cyclones hitting Maldives are destructive due to associated
- strong winds that exceed a speed of 150 kilometers per hour
- rainfall of above 30 to 40 centimeters in 24 hours<br>
- storm tides that often exceed four to five meters
Maldives is also affected
by severe local storms- thunder storm. Maldives lies near Equator
which prevents direct effects of cyclones. However, our infrastructure is
not strong enough to uphold strong winds. Therefore, even if its lower
than cyclone 3 category indirect effects can be devastating.
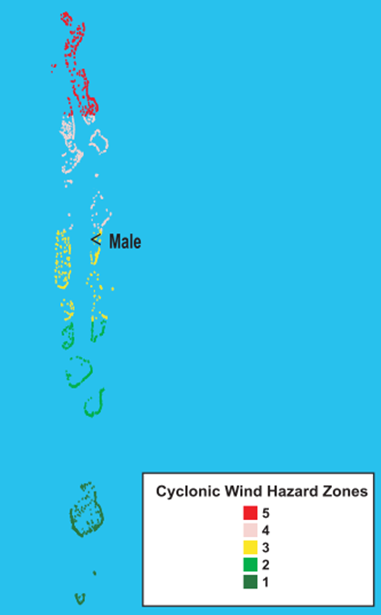
Cyclonic Wind Hazard Zones
The northern atolls are exposed to higher hazard level from cyclonic winds and their associated storm surge. The hazard level reduces gradually to very low in the southern atolls.
Heavy Rainfall
Floods occurs in a lot of islands of the country. Mostly due
to heavy rainfall in Hulhangu Moosun.
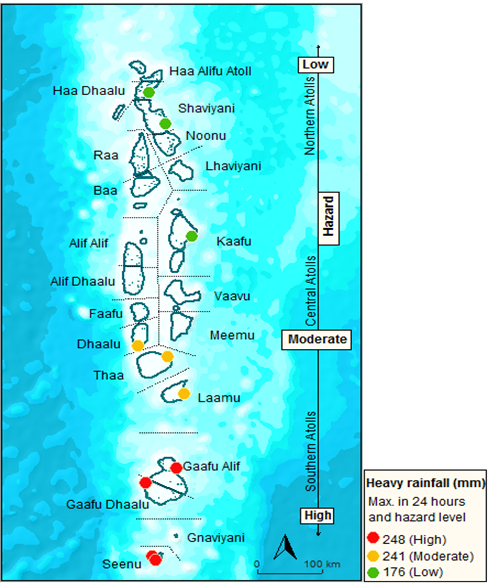
Heavy Rainfall (MM)
Severe damages are reported from islands of southern and central atolls of the country as they experience more rainfall compared to other parts of the country.
Sea Swells
Maldives also experiences
coastal flooding through swells. For example, a long-lasting swell originated
from 6000km away from the Southern Ocean and caused major flooding in April
1987that affected the following atolls: Gaafu Dhaalu, Dhaalu, Thaa and Laamu. During May-June 2014, the
tidal swells caused damages to agricultural crops in Dhihdhoo island in Haa
Alifu atoll, Nellaidhoo and Hirimaradhoo islands in Haa Dhaalu atoll, and few
other islands in Shaviyani, Noonu, Raa, Baa, Kaafu, Gaafu Alif, Gaafu Dhaalu
atolls.
Droughts (Water Shortage)
A lot of islands report
shortage of drinking water during iruvai (hot) season. Paternal changes due to
climate changes can intensify the situation as it is becoming difficult to
forecast the rainfall timings etc. Changes to lifestyle has decreased the rainwater harvesting in comparison to earlier times
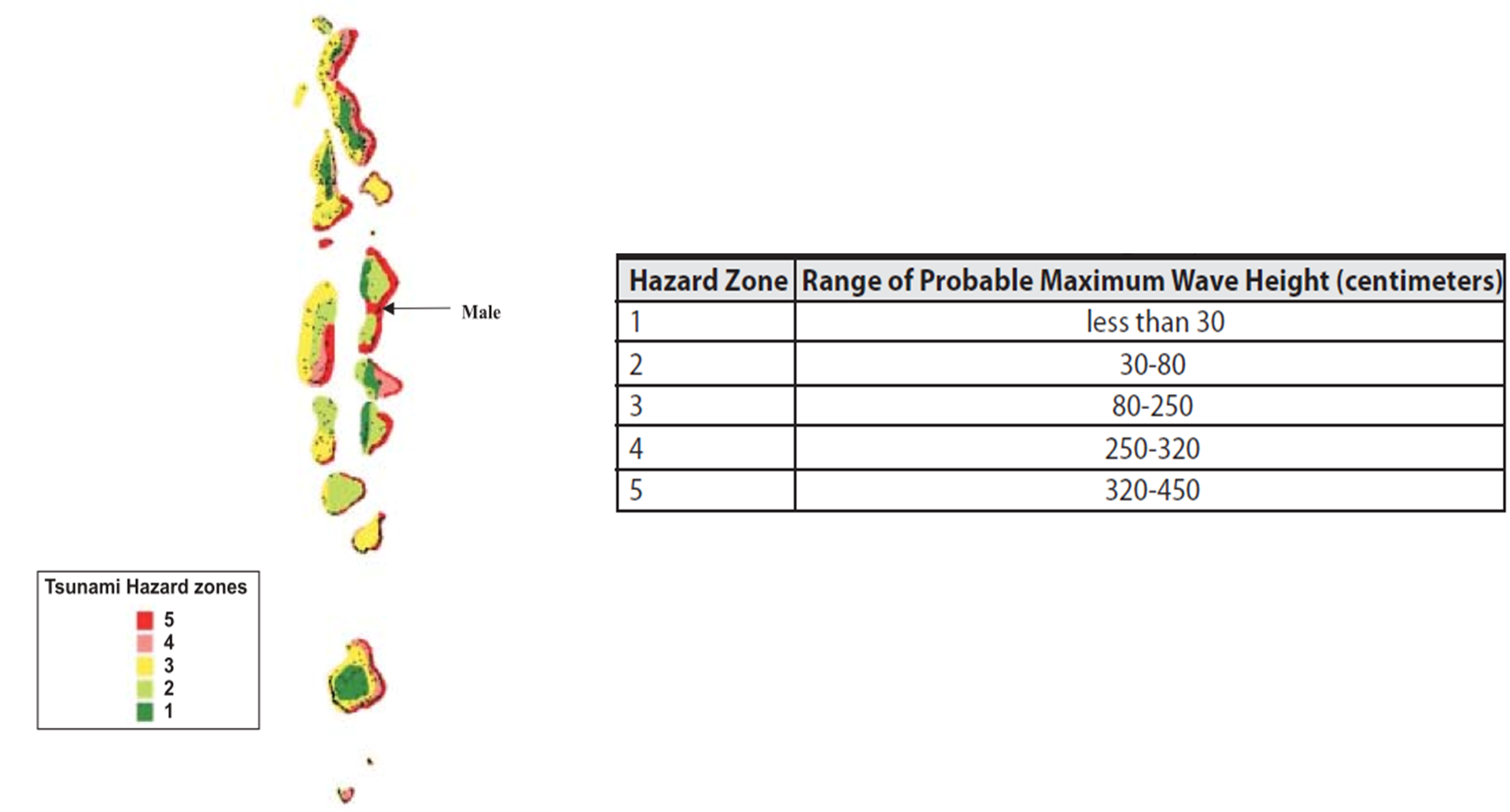
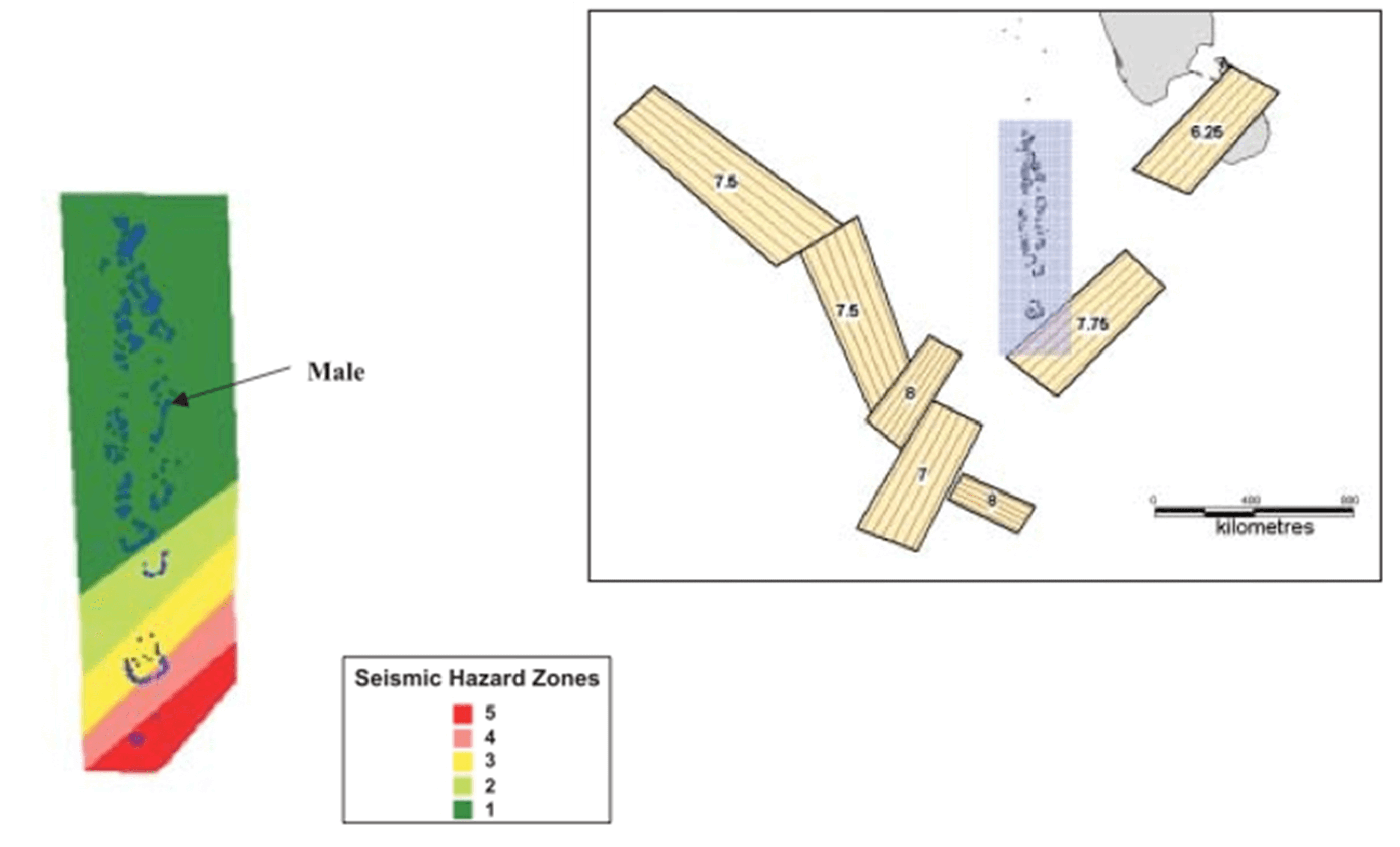
Tsunami
There are 3 significant tsunami source zones in the Indian Ocean. They are Makran coast zone, Sumatra subduction zones and Carlsberg transform fault zone. The risk of Tsunami in Maldives is particularly high along the
eastern Atolls from Sumatra subduction zone.
Earthquake
The country directly is exposed to earthquake in Carlsberg
ridge. This ridge is 600km right below
Addoo City (southernmost island of Maldives).
Fire
Fire Hazards are conditions that favor fire development or
growth. Three elements that are required to start and sustain fire (1)oxygen
(2)fuel (3)heat. Because oxygen is naturally present in earth environments,
fire hazard usually involves the mishandling of fuel or heat
Fire incidents are becoming increasingly common in Maldives,
specifically in urban areas. These incidents cause loss of lives, properties
and huge financial losses to victims. Some cases also lead to disruption of
critical services.
